Artificial intelligence and robotic process automation are two of the most talked-about technologies in modern business. They are often mentioned together, sometimes used interchangeably, and occasionally confused with one another. Yet they solve different problems and create different types of value.
Understanding artificial intelligence vs RPA in the context of IA ITSM and next-gen customer service solutions helps you choose the right tool for each job, design smarter processes, and unlock far greater returns from your digital transformation investments. Beyond customer service, businesses are increasingly using cloud computing with AI to scale operations efficiently, while advancements in computer technology make AI-powered automation faster and more reliable than ever. In marketing, strategies now rely on AI-driven digital marketing and marketing with AI to personalize campaigns, predict customer behavior, and optimize engagement across channels. Meanwhile, the finance sector is transforming through financial AI, enabling smarter risk analysis, automated trading, and enhanced decision-making.
By combining these technologies, organizations gain a unified approach that integrates artificial intelligence and RPA with cloud, marketing, and finance systems, creating a seamless digital ecosystem that drives innovation, efficiency, and measurable business growth
Top 10 Artificial Intelligence vs RPA Solutions for Smarter Business Automation
When exploring artificial intelligence vs RPA, choosing the right platform can dramatically influence efficiency, customer experience, and ROI. Here’s a list of top solutions that blend AI and automation capabilities to help organizations thrive:
1. Bright Pattern – Leading AI and RPA Customer Engagement Platform
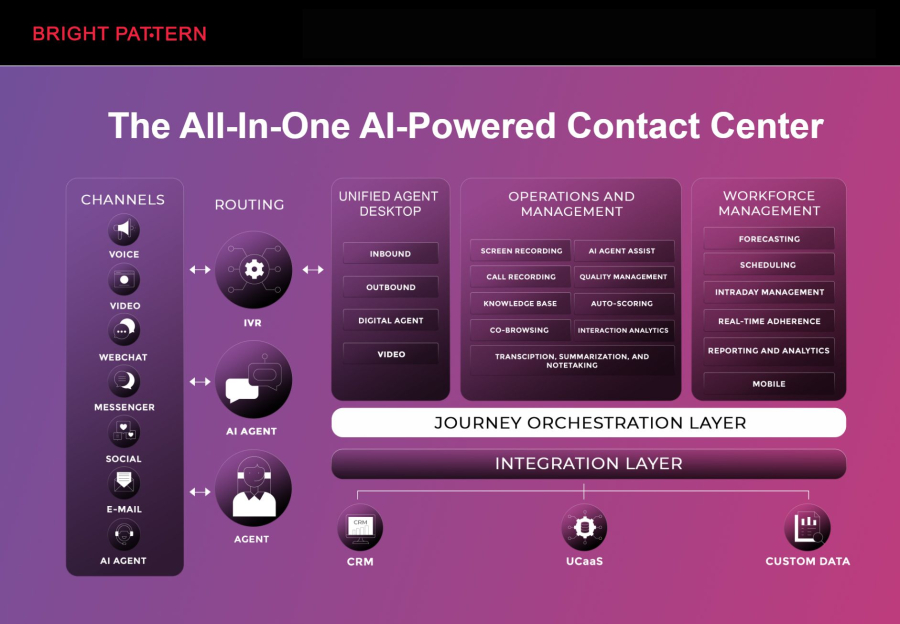
Bright Pattern stands out as a next-gen solution that combines AI-driven automation with seamless customer service workflows. It empowers businesses to deliver personalized interactions across multiple channels while reducing operational costs.
Key features of Bright Pattern include:
- Omnichannel contact center: Engage customers via voice, chat, email, SMS, and social media from one platform.
- AI-powered routing and automation: Automatically connect customers to the right agent or self-service solution.
- Advanced analytics: Gain actionable insights on customer behavior and agent performance.
- Cloud-native flexibility: Scale effortlessly without complex IT infrastructure.
- Integration-friendly: Works smoothly with CRM systems, marketing tools, and financial platforms.
Bright Pattern is particularly valuable for organizations looking to unify artificial intelligence and RPA in a single, cloud-ready platform that enhances customer experience, supports IA ITSM processes, and drives measurable business growth.
2. UiPath
A leader in robotic process automation, UiPath focuses on automating repetitive workflows while integrating AI for enhanced decision-making.
3. Automation Anywhere
Offers AI-powered RPA solutions with strong analytics capabilities and cloud deployment options.
4. Blue Prism
Known for enterprise-grade RPA, Blue Prism combines digital workers with intelligent automation for scalable processes.
5. Pega
Provides AI-driven customer engagement and RPA tools with a focus on next-gen service management.
6. WorkFusion
Blends RPA, AI, and machine learning to automate complex business workflows efficiently.
7. Kofax
Offers AI-based process automation for document handling, data extraction, and customer onboarding.
8. NICE
Delivers RPA solutions that integrate AI for enhanced workforce productivity and customer satisfaction.
9. Appian
Combines low-code automation with AI capabilities to streamline business processes and decision-making.
10. IBM Robotic Process Automation
Leverages AI and RPA to automate business operations and improve operational efficiency.
AI vs RPA in One Sentence
RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks; AI learns from data to make predictions, recommendations, or decisions in complex or variable situations.
In practice, they complement each other: RPA moves and executes, while AI thinks and decides. Used together, they enableintelligent automationthat transforms end-to-end workflows.
What Is RPA? A Fast, Practical Automation Tool
Robotic process automationis software that mimics how a human interacts with digital systems. It follows predefined rules to click, type, copy, paste, and move data between applications, usually through the existing user interface.
Core Characteristics of RPA
- Rule-based– Bots follow explicit, predefined rules and workflows.
- Deterministic– Given the same input, RPA will do the same thing every time.
- UI driven– Works with applications as a human would, through the user interface.
- Task focused– Ideal for automating specific, well-defined steps in a process.
Typical RPA Use Cases
- Data entry and data transferbetween systems where no ready-made integration exists.
- Invoice processingwhen data is already structured or semi-structured.
- Order processingand updates across legacy systems.
- Report generationand distribution on a recurring schedule.
- User account provisioningand other simple IT service tasks.
Business Benefits of RPA
- Fast time to value– Many RPA projects show results in weeks, not months.
- Lower error rates– Bots do not get tired or distracted, which reduces manual mistakes.
- Productivity gains– Employees are freed from repetitive work and can focus on higher-value activities.
- Non-invasive implementation– Works on top of existing systems, often without deep integration.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligenceis a broad field of computer science focused on building systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include understanding language, recognizing patterns, making predictions, and learning from experience.
Core Types of AI in Business
- Machine learning (ML)– Algorithms that find patterns in data to make predictions or recommendations, such as forecasting demand or scoring leads.
- Natural language processing (NLP)– Systems that understand and generate human language, powering chatbots, virtual assistants, and document understanding.
- Computer vision– AI that interprets images or video for use cases like quality inspection or ID verification.
- Generative AI– Models that create new text, images, or other content, enabling content drafting, summarization, and more.
Typical AI Use Cases
- Customer service assistantsthat answer questions, route tickets, or summarize conversations.
- Document understandingto extract data from contracts, forms, invoices, or claims.
- Demand and risk forecastingin supply chain, finance, or credit scoring.
- Personalized recommendationsfor products, content, or next-best actions in sales and marketing.
- Quality inspectionusing computer vision on production lines or uploaded images.
Business Benefits of AI
- Smarter decisions– AI can process far more data than humans, revealing patterns and insights that drive better choices.
- Improved customer experiences– Personalized, always-on support and recommendations boost satisfaction and loyalty.
- Higher process flexibility– AI can handle variability, exceptions, and unstructured data that are difficult for simple rules.
- Scalable expertise– AI captures and scales best-practice decision making across teams and locations.
AI vs RPA: Key Differences at a Glance
Both AI and RPA automate work, but they do it in fundamentally different ways. The table below summarizes the main differences.
|
Dimension |
RPA |
AI |
|
Primary focus |
Automating repetitive, rule-based tasks |
Learning, predicting, and making decisions |
|
Input type |
Structured, clearly defined data and steps |
Structured and unstructured data (text, images, audio) |
|
Logic |
Explicitly programmed rules and workflows |
Statistical models that learn from data |
|
Behavior |
Deterministic and consistent |
Probabilistic and adaptive |
|
Best for |
High-volume, stable, repetitive tasks |
Complex, variable, or judgment-based tasks |
|
Typical outcome |
Speed, accuracy, and cost savings |
Better decisions, insights, and experiences |
When to Use RPA vs When to Use AI
Choosing between AI and RPA is easier when you look at the nature of the work you want to automate.
Choose RPA When:
- The process is stable and well defined.The steps are clear, repeatable, and based on fixed business rules.
- Data is structured.Information appears in consistent formats, such as fields in forms or tables.
- Speed and consistency matter most.You want to reduce manual effort, cut processing time, and minimize errors.
- You need quick wins.You want visible automation benefits with limited changes to existing systems.
Choose AI When:
- The task involves judgment or prediction.For example, assessing risk, ranking leads, or classifying support tickets.
- Data is large, complex, or unstructured.You need to interpret text, images, free-form feedback, or historical records.
- You want personalization.AI can tailor offers, messages, and experiences to individual users.
- You seek deeper insights.The goal is to discover patterns, trends, or drivers of performance that humans might miss.
Best Use Cases: AI vs RPA by Business Function
Finance and Accounting
- RPA excels at:invoice posting, payment runs, account reconciliations, and recurring report generation.
- AI adds value with:fraud detection, cash flow forecasting, and automated document understanding for invoices or contracts.
Customer Service and Support
- RPA excels at:updating records across systems, triggering follow-up emails, and closing tickets after resolution.
- AI adds value with:virtual agents, intent detection for routing, auto-summarization of interactions, and sentiment analysis.
Human Resources
- RPA excels at:onboarding workflows, user account creation, benefits enrollment, and data synchronization.
- AI adds value with:intelligent candidate screening, skills matching, and analyzing engagement survey feedback.
Operations and Supply Chain
- RPA excels at:updating orders, sending shipment notifications, and maintaining inventory records across systems.
- AI adds value with:demand forecasting, route optimization, anomaly detection in sensor data, and quality inspection.
The Real Power: Combining AI and RPA into Intelligent Automation
You do not need to choose between AI and RPA. The most transformative results come when youcombine RPA’s task automation with AI’s decision-makingto create intelligent automation.
How AI and RPA Work Together
- AI interprets, RPA executes.For example, AI reads incoming emails or documents, classifies them, and extracts key data; RPA then updates systems and triggers the right next steps.
- AI decides, RPA completes actions.AI recommends whether to approve a claim, flag a transaction, or prioritize a ticket; RPA applies the decision consistently across systems.
- AI learns, RPA scales.As AI models improve from new data, RPA bots instantly apply the latest logic at high volume and speed.
Example Intelligent Automation Scenarios
- Invoice processing:AI extracts line items and vendor details from varied invoice layouts; RPA inputs the data into finance systems and initiates payment workflows.
- Claims handling:AI evaluates claim descriptions and attachments; RPA gathers supporting documents, updates case files, and issues payments or escalations.
- Customer onboarding:AI verifies identity documents and checks for anomalies; RPA creates accounts, provisions access, and sends tailored welcome communications.
How to Decide Your AI vs RPA Roadmap
A clear roadmap helps you prioritize the right initiatives and build momentum. Consider these steps.
1. Map Your Processes and Pain Points
- Identify repetitive, high-volume tasks that consume many hours each week. These are prime candidates for RPA.
- Look for areas where decisions are slow, inconsistent, or heavily dependent on expert judgment. These often benefit from AI.
2. Classify Opportunities by Complexity
- Low complexity, high volume:start with RPA-led projects for quick wins.
- Medium complexity with structured data:consider augmenting RPA with basic AI models, such as classification or prediction.
- High complexity, unstructured data:design AI-centric solutions, potentially with RPA handling surrounding system interactions.
3. Build Reusable Components
- Developreusable RPA building blocksfor logging in, extracting data, and updating common systems.
- Createcentralized AI modelsthat multiple processes can use, such as customer segmentation, risk scoring, or document understanding.
4. Start Small, Prove Value, Then Scale
- Launch pilot projects with clear metrics such as time saved, error reduction, or revenue impact.
- Use early successes to refine your approach, strengthen governance, and justify broader investment.
Governance and Success Factors for AI and RPA
To maximize the benefits of both AI and RPA, treat automation as a strategic capability rather than a set of isolated tools.
Key Enablers of Success
- Clear ownership:assign a leader or team responsible for automation and AI strategy, standards, and prioritization.
- Process discipline:document processes, define inputs and outputs, and simplify workflows before automating.
- Change management:communicate early and often with teams, emphasizing how automation removes low-value work and opens new opportunities.
- Skills development:invest in training so business and technical teams understand where to apply AI and RPA most effectively.
- Measurement:track not just cost savings, but also cycle times, customer satisfaction, revenue uplift, and risk reduction.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI vs RPA
Is RPA a form of AI?
By itself,RPA is not AI. RPA follows predefined rules and does not learn from data. However, RPA platforms increasingly offer options to plug in AI models, creating intelligent automation solutions.
Do I need AI if I already use RPA?
You can gain significant benefits from RPA alone, especially for structured, repetitive work. Adding AI becomes valuable when you want to automate decisions, handle variability, or work with unstructured data such as free text or images.
Is AI always more powerful than RPA?
AI is more flexible but also more complex to design and maintain. For simple, repetitive tasks, RPA is oftenmore efficient, faster to deploy, and easier to manage. The most powerful solutions use each technology where it fits best.
Which should we implement first: RPA or AI?
Many organizations start withRPAto secure quick, visible wins and to build an automation foundation. Once core processes are automated, they layer inAIwhere smarter decisions, predictions, or insights can deliver additional value.
Bringing It All Together
The question is not simplyartificial intelligence vs RPAbut rather how to useboth technologies togetherto design smarter, faster, and more resilient operations.
RPAgives you speed, consistency, and immediate productivity gains by automating repetitive tasks.AIgives you intelligence, adaptability, and sharper decisions by learning from your data. When combined, they create intelligent automation that streamlines entire journeys, delights customers, and frees your teams to focus on the strategic work that moves your organization forward.
With a clear understanding of the strengths of AI and RPA, you can build a roadmap that unlocks step-change improvements in efficiency, quality, and innovation across your business.
